Lotyšsko
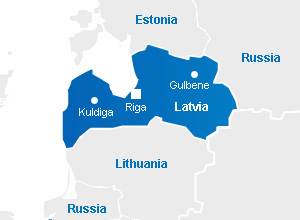
Situated in north-eastern Europe with a coastline along the Baltic Sea, Latvia has borders with Estonia, Russia, Belarus and Lithuania.
It has linguistic links with Lithuania in the south and historical and religious ties with Estonia in the north.
Total area: 64,589 sq km (slightly larger than West Virginia)
Population: 1.8 million
Government type: Parliamentary democracy
Administrative division: 110 municipalities (called „novads“) and 9 republic cities
Capital + other major cities: Riga (614,000) + Daugavpils (79,000), Liepaja (67,000), Jelgava (55,000)
Currency: Euro (since January 2014)
Languages: Latvian (official) 56.3%, Russian 33.8%, other 0.6% (includes Polish, Ukrainian, and Belarusian), unspecified 9.4%
Ethnicity:Latvian 62.7%, Russian 25.5%, Belarusian 3.1%, Ukrainian 2.2%, Polish 2%, Lithuanian 1.1%, other 1.8%, unspecified 2.6%
Religion: Lutheran 36.2%, Roman Catholic 19.5%, Russian Orthodox 19.1%
President: (Mr.) Edgars RINKĒVIČS (since 8 July 2023)
Prime Minister: (Ms.) Evika SILIŅA (since 15 September 2023)
Date of EU accession: 1 May 2004
KEY FEATURES
- One of the richest forestry resources in Europe
- Most of Latvia’s territory is less than 100 m (330 ft) above sea level
- Among the world’s greenest countries
- Highest share of renewable energy production in CEE
- More than 25% of the population is Russian-speaking
- One of the most wanted FDI destinations in Europe
- Exports contribute to nearly a third of the GDP
- Corruption and low birth rate are major challenges to economic vitality
- The poorest country among the Baltic States
- Significant port facilities in Riga, Ventspils, and Liepāja
MACROECONOMIC OVERVIEW
Since its independence, Latvia has implemented market-oriented reforms. The country’s economy has performed well due to steady growth in domestic consumption and the contribution of foreign investment. As a member of the EU since 2004 (and of the Eurozone since 2014), the country has benefited from substantial European funding. The country’s economy was severely affected by the financial crisis and although it returned to positive growth in the second decade of the 21st century, it has never reached its pre-crisis growth rate. The growth has been mainly driven by household consumption and public spending (including EU funds). Latvia’s economy has been affected by the EU sanctions imposed on Russia and disruptions in international supply chains posing a new challenge for the future.
Latvia’s macroeconomic indicators are generally positive as the country pursued tax and labour reforms following its stability programme. Public debt is among the lowest in the EU and inflation has been rather steady until 2022. Foreign Direct Investment in Latvia is currently rather moderate, as are exports.
The unemployment rate has been falling since 2010 (19.5%) and is expected to decrease further in the upcoming years. Nevertheless, the Latvian economy is negatively impacted by a demographic challenge: the country has one of the lowest population growth rates in the EU (est. -1.11% in 2022), with birth numbers declining continuously. In addition, Latvia has to face a strong emigration of skilled young people. Both the largest cities and the countryside have experienced population losses with hundreds of villages left abandoned, according to National Land Offices. The government is trying to partially offset these issues by increasing the retirement age by three months each year (to reach age 65 in 2025).
Selected economic indicators, Latvia, 2017 - 2023
| 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | ||
| GDP |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| Real GDP growth |
%
|
3.3 | 4.0 | 0.6 | -3.5 | 6.7 | 3.0 | -0.3 |
| GDP at current prices |
€ bn
|
26.8 | 29.06 | 30.48 | 30.26 | 33.61 | 38.3 | 40.3 |
| Foreign trade |
|
|||||||
| Exports |
€ bn
|
16.61 | 17.92 | 18.33 | 17.8 | 21.05 | 27.84 | 25.84 |
| Imports |
€ bn
|
16.78 | 18.12 | 18.55 | 17.45 | 21.74 | 29.76 | 27.4 |
| Balance |
€ bn
|
-0.17 | -0.2 | -0.21 | 0.34 | -0.68 | -2.27 | -1.55 |
| Prices |
|
|||||||
| CPI – average inflation rate |
%
|
2.9 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 0.1 | 3.2 | 17.2 | 9.1 |
| PPI – industry – average |
%
|
2.3 | 5.5 | 3.6 | -3.2 | 12.5 | 49.5 | 1.7 |
| Employment |
|
|||||||
| Registered unemployment |
%
|
8.7 | 7.4 | 6.3 | 8.1 | 7.6 | 6.9 | 6.5 |
| Average monthly gross wage |
€
|
926 | 1,004 | 1,076 | 1,143 | 1,227 | 1,373 | 1,537 |
Source: Central Statistics Bureau of Latvia, IMF, OECD, World Bank, Eurostat, 2017-2023
KEY SECTORS
The agricultural sector contributes 3.6% of the GDP and employs 7% of the active population. It is dominated by cattle breeding and dairy farming, in addition to the production of grain cereals (barley, wheat, rye, oats), sugar beets, potatoes and vegetables. Almost 39% of Latvia’s territory is destined for agricultural use. Since the early 1990s, the structure of land management changed significantly. Nevertheless, the competitiveness of agriculture in Latvia is still low, compared to other EU countries. Apart from timber, which is largely exported, Latvia has almost no natural resources. Fishing and forestry are also important components of the primary sector. The country has a long tradition of fishing, which began during Soviet times. Traditionally, fish such as salmon and trout are predominantly caught. However, in recent years, the government has taken action to protect valuable fish stocks and various fish farms have been set up.
The industrial sector contributes to 19.5% of the GDP and employs almost one-fourth of the active workforce (23%). The construction, metallurgy, industrial food-processing, and mechanical engineering sectors are booming. Latvia is well-known as an important producer of railway equipment, radios, refrigerators, medicines, timber and steel by-products. The manufacturing sector is estimated to account for 10.6% of total GDP.
The Latvian economy is driven by the service sector which contributes to 64% of the GDP and employs 70% of the active population. Thanks to its attractive fiscal regulation, Latvia has developed a large financial service sector. Nonetheless, the corporate tax rate, which was one of the lowest in the EU, has been raised to 20% recently. Transportation and ICT are also important sectors of the country’s economy.
Forestry & Wood Products
Forest covers almost 50% of the national territory and Latvia has one of the richest forest resources in Europe. About 50% of forests are state-owned. These industries contribute approximately 20% of the GDP of the manufacturing industry. This is one of the main reasons Latvia has a significant export industry; wood products account for one-third of total exports. The main product groups are energy wood, and packaging materials, construction timber, joinery and carpentry products, furniture and wooden houses.
Food Processing & Beverages
Almost a quarter of the total manufacturing turnover is accounted for the food industry which is one of Latvia’s richest industries. The food processing industry covers 29% of Latvia’s industrial capacity.
75% of the products are sold within Latvian borders, the food processing industry is therefore the least-exported industry in Latvia. The main sub-industries are milk processing, drinks, fish processing and meat processing. The most important benefit of Latvia’s food processing and beverage sector include accessibility of high-quality raw materials, stable domestic demand, price competitiveness within Western markets and high product acknowledgment in the Russian market.
ICT
The IT industry is Latvia’s fastest-growing industry sector with an annual growth of 20-30%. In recent years exports from the IT sector have risen rapidly, growing annually by approximately 15%. The industry has benefited from having a well-qualified workforce that has gained expertise in IT. In addition, the mobile industry has developed which is due to expertise in the IT industry. Latvian companies have benefitted from outsourcing opportunities from large IT firms such as IBM, Microsoft, and Unisys, and various Latvian companies have been acquired by companies such as Exigen, TietoEnator. The global business services and shared service centres are also developing rapidly, with Scandinavian firms at the forefront, choosing Latvia as a prime location for its language skills, cost-effectiveness and cultural compatibility.
Chemicals
The sector accounts for 10% of the manufacturing industry. It has a strong R&D capability, particularly in the pharmacy, recycling sector, green chemicals and bio cosmetics which contribute to the country's high exports.
Transport and logistics
The largest service sector accounting for 7.2% of the country’s GDP. Latvia benefits from its geographical location, excellent infrastructure and diversified transport services combining rail, sea, and road transport.
Metal Processing and Mechanical Engineering
The industry has a long tradition in the country, which used to serve as one of the technologically advanced manufacturing centers of the Soviet military and aerospace industries. Today, the sector accounts for 20% of total manufacturing exports, exporting almost 70% of its total output and specialising mainly in value-added products in the fields of electronics, medical machinery and equipment, precision mechanics and optical instruments.
EXPORTS & IMPORTS
Latvian exports contribute to nearly a third of GDP (the GDP/export ratio in 2022 was 70.4%). Most of their export go to EU countries, and the share of imports from EU countries stands at 73.1%.
2023 export and import data:
Main import partners:
Lithuania – 21.2%
Germany – 11.1%
Poland – 10.6%
Estonia – 8.5%
Netherlands – 4.3%
Main export partners:
Lithuania – 18.1%
Estonia – 11.6%
Germany – 7%
Russian Federation – 6%
Sweden – 5.9%
United Kingdom – 4.8%
Market Research in Latvia
EasyLink provides professional expertise in strategic market research, market intelligence, competitive intelligence, market size analysis and market potential evaluation, competitive landscape and distribution structure study, identification of new customers and potential partners etc. Please contact us to discuss how we can assist your business objectives in export, marketing or sourcing.
Customer Search & Partner Search in Latvia
We are experienced experts in matchmaking projects involving the search, identification, screening and pre-selection of business partners in Central & Eastern Europe, ranging from distributor search to profiling of prospective customers and identifying specific business opportunities; we assist our clients with sourcing in emerging markets and low-cost markets in the CEE region.
International Trade Consultancy – Export, Marketing and Trade Promotion in Latvia and the Baltic region
EasyLink has a unique track record in international trade promotion. With local consultants in all key markets in Central & Eastern Europe, EU markets and some overseas markets, we provide customized market research, develop trade opportunities with prospective partners and new customers, and assist clients with strategic advice for their export, marketing and sourcing needs.